
This site is a work in progress and will continue to change as our software evolves. Every effort will be made to publish updates promptly as they are released. Please email any questions or comments to pburgio@foscd.com.
Glossary of Terms #
Action Cost #
The total price of a specified quantity of a component, assembly or system to be repaired or replaced multiplied by the unit cost. (See Unit Cost)
Action Timeframe #
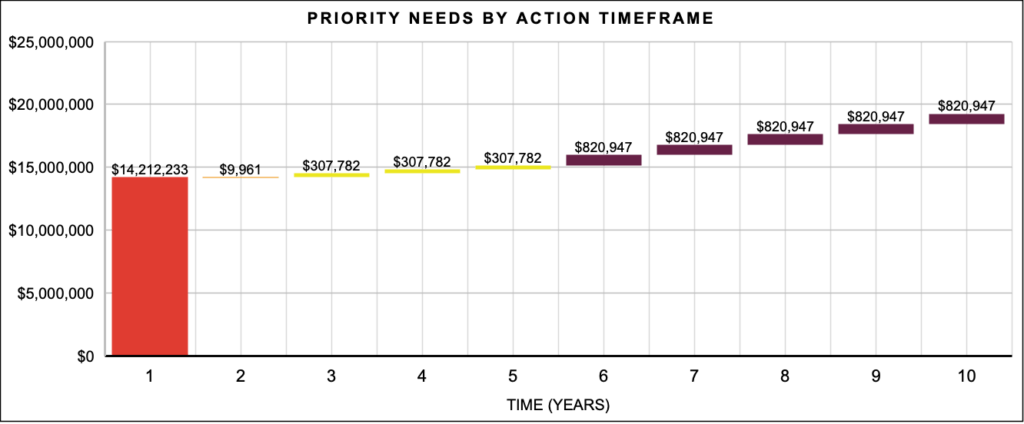
The recommended window of time in which to make a repair or replacement. Pictured below, a sample of Priority Needs by Action Timeframe.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 #
Federal civil rights legislation that prohibits discrimination and ensures equal opportunity for persons with disabilities in employment, State and local government services, public accommodations, commercial facilities, and transportation.
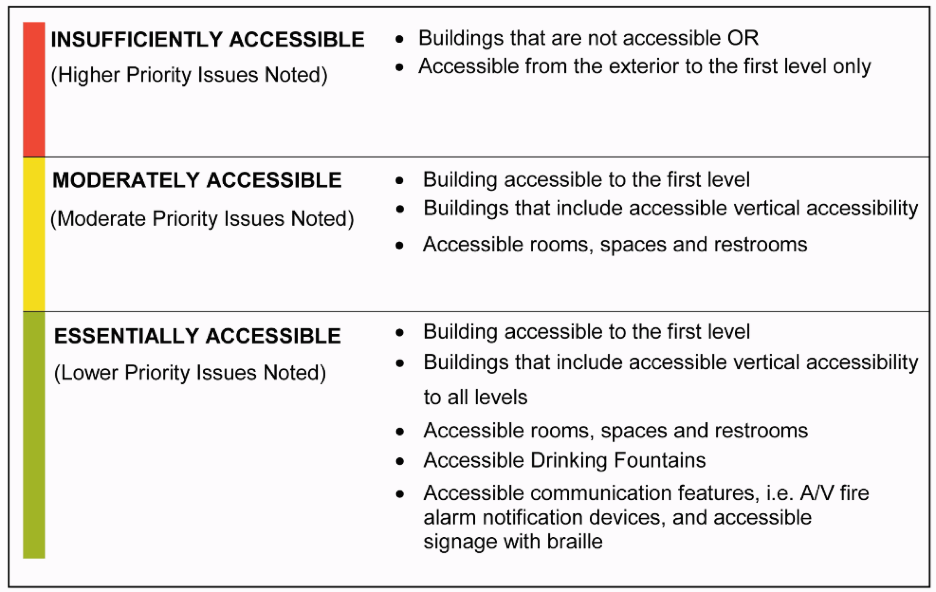
ADA Accessibility Ranking System #
A ranking for each asset will be assigned an ADA rank of Essentially Accessible; Moderately Accessible; or Insufficiently Accessible.
Adjustment Factor #
Utilized to allow for customized estimating or atypical applications.
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) #
A private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States.
American Standards for Testing and Materials (ASTM International) #
Originally founded in 1898, the American Standards for Testing and Materials is now known as ASTM International, an organization that develops international standards for materials, products, systems, and services used in construction, manufacturing, and transportation.
Assembly #
A group of parts or components that fit together to form a self-contained unit or system.
Asset #
A building or structure, a portion of a structure, or any part of facility infrastructure that is distinguishable from its surroundings by use, date of construction, construction type, specific systems or other factors that make it an identifiable portion of the owner’s property .
Below the Line Costs #
Costs related to furnishings, fixtures, and equipment that are typically provided by the owner outside of a construction project but need to be included before the building can be utilized for its intended purpose.
Beyond Useful Life #
The period past which a building component, assembly, or system in a building or facility is expected to be useable for the purpose for which it was intended. Some building components, assemblies, or systems may continue to function indefinitely but may be at greater risk of failure, and maybe operating at a reduced efficiency (see ‘Useful Life’ entry for related information).
Building Gross Square Footage (BGSF) #
The total space in square feet calculated from the exterior perimeter of the building per level. In a one story building this is also referred to as the building footprint. This is always greater than the net square footage as it includes the thickness of exterior walls.
Building Owners and Managers Association International (BOMA) #
BOMA publishes industry-recognized building equipment and materials ‘lifecycle’ standards that should be referenced for ‘lifecycle expectancy’ per each assessment item contained within a UniFormat-based deficiency (see Lifecycle entry for more information).
British Thermal Unit (BTU, MBTU, MMBTU) #
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. BTU is most often used as a measure of power in steam generation, heating, and air conditioning. The unit MBTU is defined as one thousand BTUs, and should not be confused with MBH which is the number of thousands of BTUs produced in one hour. MMBTU denotes one million BTUs.
Capital Improvement (or Capital Renewal) #
The addition of a permanent structural improvement, addition, restoration, or replacement of a component, assembly, or system of a property that will either enhance the property’s overall value or increases its useful life.
Category #
The primary thematic group used in a Facility Suitability Assessment (FSA) as a major classification division. Categories generally include Educational Program, Technology, Safety and Security, Wellness, Relationships and Collaboration, and Operational Utility. The FSA Rubric is divided into Categories and then a subgrouping of KPIs and Measures.
Category Suitability Index (CSI) #
CSI is established through a defined priority hierarchy of pre-determined goals and objective requirements for each Category within a facility or portfolio. Each Category is weighted through the implementation of a Rubric to determine CSI scores. CSI = KPI score multiplied (*) by the KPI Index value (in percentage based on value assigned) divided by (÷) the total number of KPIs in that Category. This index is user-customizable.
Component #
An item found within a system that forms an operational portion of a building or facility. For example, a mechanical system has many components including diffusers, piping, controls, as well as assemblies that include ductwork and dampers, and equipment including air handlers, chillers, and boilers. The respective components when combined describe a ‘system.’ (See System entry for related information.)
Computer Maintenance Management System (CMMS) #
A sophisticated software platform that is used in the scheduling of general, routine, and or preventative maintenance work and provides work ticketing as well as completion tracking to ensure routine/preventative maintenance objectives are followed and warranties do not become invalid (when applicable) due to neglect. Manufacturers of service equipment as well as materials often post maintenance requirements for their respective products. This information is often imported and utilized within a CMMS system
Condition #
A general ranking of ‘Good, Fair, Poor, Critical, or Divest’ as assigned by field assessor staff to a system or component within an asset.
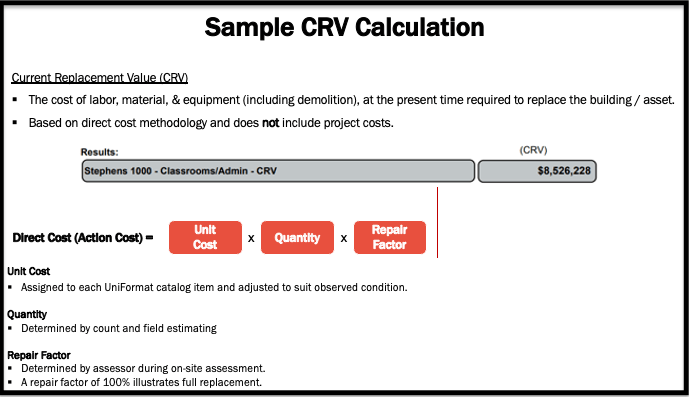
Current Replacement Value (CRV) #
The cost of labor, material, and equipment, (including demolition) at the present time which would be required to replace a building or asset. The CRV is based on direct cost methodology and does not include project costs such as design, general conditions, a contractor’s overhead and profit, or land acquisition. This value assumes replacement of an asset including demolition on a ‘greenfield’ site. Other specialty or non-project related costs such as hazardous materials, suitability, move-management are considered ‘below-the-line.’
CRV Accuracy #
The accuracy of the CRV is critical for RDM programs.
- If CRV is high the FCI condition is overstated. This results in lower-than-necessary funding and hidden liabilities.
- If CRV is low the FCI condition is understated. This results in overstated liabilities and the potential for misallocation of resources or possible over-spend.
Construction Specifications Canada (CSC) #
Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) #
Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) #
A unit of volumetric capacity. It is commonly used by manufacturers of blowers and compressors. CFM typically relates to air flow through, in or out of a given system or unit.
Discipline Condition Index / System Condition Index (DCI / SCI) #
Discipline Condition Index / System Condition Index are industry-standard indexes that objectively measure the current condition of all building components, assemblies, or service systems within an asset. DCI and SCI both utilize the UniFormat classification system.
SCI = Repair or Replacement Cost ÷ Replacement Value (of a system, and may also be utilized for component, or assembly.)
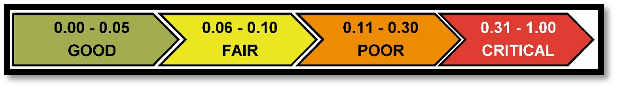
Discipline Condition Index / System Condition Index is a similar scale to the Facility Condition Index scale is used in describing DCI and SCI. The two major differences between the FCI scale and the DCI / SCI scale shown below is that the “Divest” ranking has been omitted, and the “Critical” score has been expanded to 1.00. The reason for these changes is to illustrate that an asset’s systems or disciplines cannot be divested. They usually require full replacement to enable the asset to function as originally designed and intended.
DCI / SCI Scale: Below is an of the DCI and SCI scale.The difference between the FCI and DCI scale is the DCI scale does not contain the “Divest” category as mentioned previously.
Deferred Maintenance #
Upkeep to a building or asset that has been postponed. The cost of deferred maintenance is an amount needed but not yet expended for repairs, restoration, or rehabilitation of an asset.
Deferred maintenance is included in the numerator of the FCI calculation.
Deferred maintenance should not be confused with general maintenance as deferred maintenance is not routine in nature (see Maintenance / Routine Maintenance / Preventative Maintenance).
Deferred maintenance may be budgeted for but has not received funding to date.
Deferred Maintenance Deficiency (DMD) #
Components, assemblies, and systems in a vertical (building) asset or horizontal (infrastructure) asset that are at risk of failing, have failed, or are beyond their useful life, and in need of maintenance, repair or replacement. DMDs are typically seen in greater frequency in older facilities requiring corrections to maintain infrastructure, systems and components and do not necessarily reflect the level of effort of maintenance initiatives. DMDs are typically identified with specific measurable information such as description, critical issue, and recommendation, as well as a cost component for curing the deficiency (direct cost methodology) that will be used to calculate and report within the software.
Deficiency #
An inadequacy in a building component, assembly, or system that needs repair, renewal, or replacement.
Depreciation #
Calculation by which an asset is depreciated; a reduction in the value of an asset with the passage of time, due in particular to wear and tear.
Discipline #
Refers to knowledge areas in architecture and engineering that are applied to buildings and facilities. Disciplines are organized utilizing UniFormat and are categorized as:
- (H-10) ADA Assessment (when applicable)
- (C-20) Architectural
- (D-60) Communications
- (D-50) Electrical
- (D-40) Fire Protection
- (D-30) Mechanical
- (D-20) Plumbing
- (D-70) Safety and Security
- (B-10) Structural
Direct Cost Methodology vs. Project Costs #
Direct Costs: the industry standard measure to apply the FCI, DCI, or SCI values consistently across deficiencies that are identified, understood and defined by FOS of CannonDesign as ‘replacement’ costs based upon the sum of units, and not based upon Project Costs to accomplish the replacement of those components. Project Costs should be anticipated to be between 40% and 60% higher than direct costs depending on the project-specific delivery methods.
Project Cost Loading: project costs are customized to match the delivery method and typically include general conditions and other soft costs including contingencies, design costs, permitting costs, bid phase costs and contractor’s overhead and profit. Project costs are not the basis for Facility Condition Assessments.
Direct Cost #
The result of Unit Cost multiplied by quantity and the Repair Factor.
Direct Cost Loading #
Direct costs include all labor and material required for the component, assembly, or system replacement. A direct cost typically includes incidental work or materials not specifically identified such as demolition, piping and ductwork connections, controls, HVAC balancing and electrical connections. Direct cost items do not include work required elsewhere within the building or site such as the partial cutting and patching of a ceiling assembly accessing a component scheduled for replacement. Clear delineation is necessary to avoid double counting for multiple system replacements. Direct costs typically do not include general contractor or construction manager (GC/CM) overhead and profit but do include sub-contractor overhead and profit. Direct cost further excludes soft costs, escalation, inflation and any overtime or off-hours work. Additional project costs including coordination costs, escalation, and any premiums for working conditions are also not considered as part of direct costs.
Expanded examples of excluded costs within Direct cost are:
- Equipment mobilization to ‘hard to access’ locations
- Architectural or structural remodel work required to accommodate MEP equipment replacement
- Overtime work rates (although we acknowledge this is often required within healthcare, and other mission-critical facilities)
- Timing of work or escalation impact
- Commissioning
- Design
- ADA compliance assessments or ADA upgrades triggered by permitting project work with Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJ)
- Life Safety/Code compliance assessments or Life Safety/Code compliance upgrades triggered by permitting project work with Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJ)
Escalation #
Escalation is an increase in the cost of a product, service, or commodity over time. It is similar to the concept of inflation except that cost escalation is specific to a particular type of cost as opposed to the economy as a whole. In the context of facility assessment data, escalation should accurately represent the expected rise in cost over time of building materials and labor, which may be substantially higher or lower than the inflation rate in the economy.
Facility #
A structure, building and/or infrastructure system that supports activities and or operations for its owner(s).
Facility Conditions Assessment (FCA) #
A process that creates a non-biased collective visual observation/inspection and provides a subsequent report of deferred maintenance issues within a select asset or group of horizontal or vertical assets.
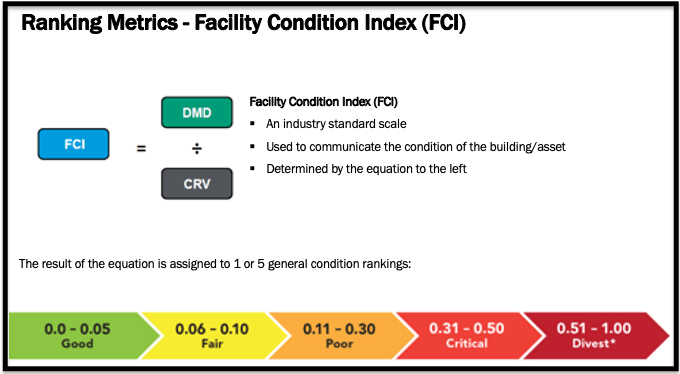
Facility Condition Index (FCI) #
An industry-standard index that objectively measures the current condition of a facility, allowing comparison both within and among other facilities. Lower FCI values represent an asset in better condition; and conversely, higher FCI values represent an asset in worse condition.
To determine FCI for any given asset, the total cost of remediating deferred maintenance deficiencies (DMDs) is divided by the current replacement value (CRV) expressed mathematically as:
DMD ÷ CRV = FCI. Example:
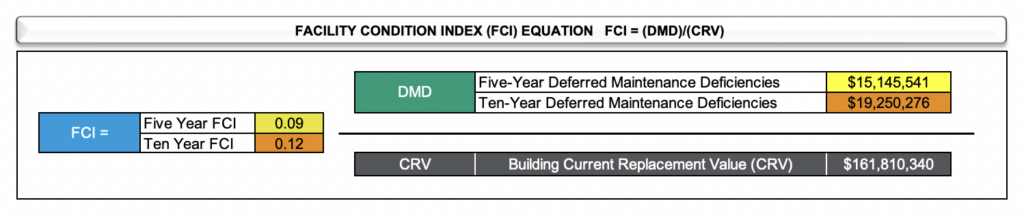
Accuracy of the FCI depends on the quality of the data found contained within the DMD and CRV, respectively. There are various approaches and scalable solutions that revolve around establishing the DMD and CRV figures, with varying degrees of accuracy that have a direct impact on FCI accuracy.
The FCI is further clarified by adding the estimated value for all the assessed Deferred Maintenance Deficiencies (DMDs) by assigned Priority of Funding Needs. Priority 1 contains assessment year 1, Priority 2 and 3 contain years two though five and Priority 4 contains years six through ten. These two number sets are then grouped into three value categories: The 1-year, 5-year, and 10-year DMDs. These numbers are each divided by the Current Replacement Value (CRV) of the asset. This is the resultant percentage from the DMD (divided by) CRV in the FCI equation. The best FCI is stated as 0.0 with the worst score stated as a 1.0.
FCI Scale #
The industry standard FCI scale is divided into five categories; Good; Fair; Poor; Critical; and Divest. These Conditions contain numerical percentages that are the result of the FCI equation represented with 2 decimal places.

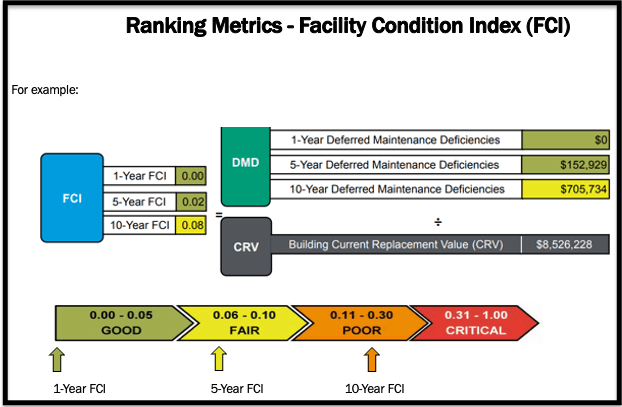
Facility Quality Index (FQI) #
The FQI equation is a representation of the FCI (in percentage based on $) multiplied (*) by the FSI index value (presented as a weighted rubric final score) divided by (÷) CRV.
Facility Suitability Index (FSI) #
While this index is user-customizable, an FSI is established through a defined priority hierarchy of pre-determined goals and objective requirements for different types of space within a facility or portfolio. These criteria are weighted through the implementation of a rubric to determine FSI Category scores. FSI = Category score multiplied (*) by the Category index value (in percentage based on value assigned) divided by (÷) the total number of Categories.
The structure consists of select thematic Categories, each Category is defined using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and then each KPI has one or more Measures that are the definitive data collected. The Measures themselves form the data collection rubric by which all facilities are scored. At the Category and KPI levels these criteria are assigned a Category weight (Categories compared against the other Categories) and a KPI weight (KPIs in a single Category compared against the other KPIs in the same Category). This allows an overall facility score to be calculated – the FSI, and an individual Category score – the CSI.
The establishment of an FSI also leads to the capability to establish a Facility Quality Index (FQI). The FQI equation is a representation of the FCI (in percentage based on $) multiplied (*) by the FSI index value (presented as a weighted rubric final score) divided by (/) CRV.
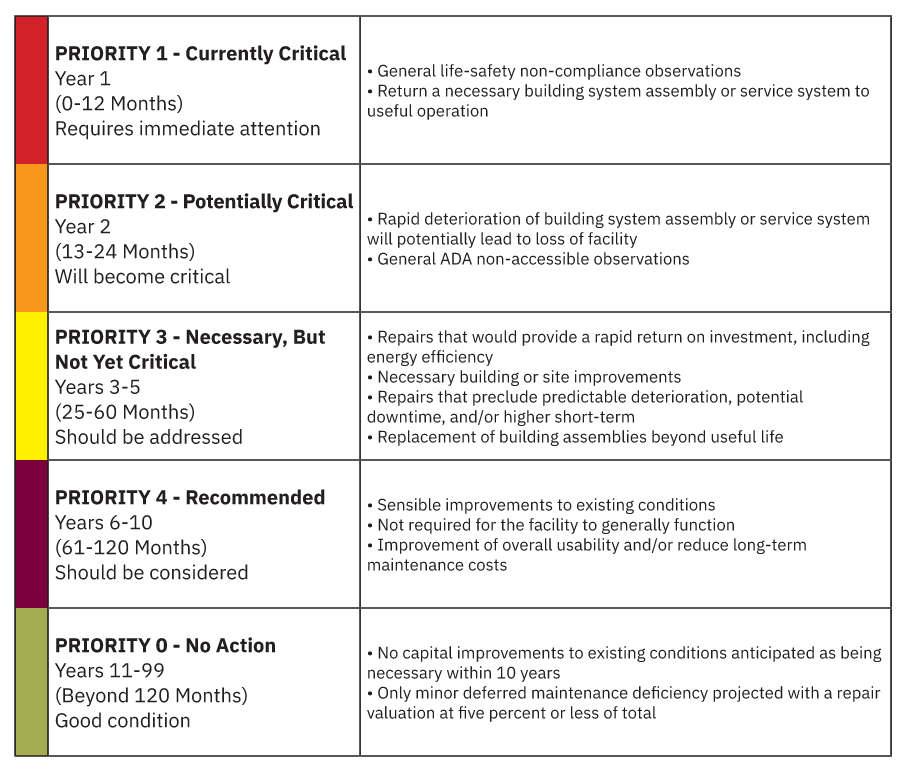
Funding Needs #
By Priority, Year, and Term: Each priority group includes the assessed DMD that falls into each respective term regardless of the discipline. Detailed descriptions of observed issues, recommendations, and associated costs will be included within the assessment effort and subsequent asset report.
Priority Definitions and Action Timeframes: priorities are cataloged as 1 through 4 (shown below). Priority 1 includes Year 1 Action Costs which are considered ‘Immediate’ funding needs. Priority 2 includes Year 2 Action Costs and are considered ‘Short-Term’ funding needs. Priority 3 includes Year 3 to 5 Action Costs and are also to be considered ‘Short-Term’ Funding Needs. Priority 4 includes Year 6 to 10 Action Costs and are considered ‘Long-Term’ funding needs.
General Maintenance #
Maintenance that is considered routine or as part of manufacturer’s recommended scheduled maintenance requirements. Generally, this can also be related to warranty maintenance requirements.
Grandfathered #
A provision in a statute or building code that exempts conditions, components and/or systems in a building from new regulations that would otherwise prevent continued use of those items. Typically, building codes allow for some individual in-kind replacements of components, but most renovation activities of assemblies and systems, including additions and new construction, trigger replacements with current code-compliant components, assemblies, and systems.
Impact of Failure #
The effect a component, assembly or system’s malfunction or ceased operation would have on the asset to which it serves.
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) #
A secondary group used in a Facility Suitability Assessment. KPIs are found as divisions under each Category to group similar Measures.
Lifecycle #
A reference standard (typically stated in years) that establishes the useful lifespan of a component or system spanning from the installation or commissioning date of an assessment item to the year of replacement. BOMA is an industry recognized standard that can be applied as a reference to an assessment item. Please see the ‘BOMA’ entry for more details.
Maintenance (Routine Maintenance, Preventative Maintenance) #
The effort required to keep a component, assembly or system in a building or facility in good working condition and functioning to the proper level for which it was intended to perform (see CMMS entry related information).
MasterFormat® #
Sometimes referred to as the ‘Dewey Decimal System’ of building construction, MasterFormat® is a product of the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) and Construction Specifications Canada (CSC) respectively. [© 2016-2018 The Construction Specifications Institute, Inc. (CSI).] The trademark MASTERFORMAT® and the copyrighted MasterFormat work are used under license from CSI (http://www.csiresources.org).
Measure #
Used to label the data collection point under a KPI in a Facility Suitability Assessment rubric. A measure may be collected from static documents or in the field. A measure is scored using either quantitative identification, generally considered objective – count, linear feet, square feet, yes/no; or using a qualitative identification generally considered subjective because it compares qualities or characteristics with a scaled score such as ranking 1-5 or 1-10 or any variation of terms such as good, fair, poor.
Modeled Aggregate #
A method used to capture the value of items that are not included in deficiency records.
Priority Assignment #
An assignment of a funding amount needed in a given calendar year or group of years and further defined by a recommended term need i.e., immediate, short-term, or long-term (see the Funding Needs entry for more information.)
Project Cost #
Customized to match the delivery method and typically include general conditions and other soft costs including contingencies, design costs, permitting costs, bid phase costs and contractor’s overhead and profit. Project costs are not the basis for Facility Condition Assessments.
Project Plan Reports #
May be generated on-demand using the software system. Projects are comprised of groups containing like or interdependent systems that exist throughout one or many assets. These projects could be stand-alone or combined to achieve efficiency through an economy of scale in both design and construction. Potential projects also should consider including any adjacent or related system, especially one nearing the end of it its service life. This allows systems replacement projects to be grouped by area and limit future occurrences of proposed work impacting recently completed work.
Project detail tables shall be provided for each project group. These are the first steps in beginning the necessary maintenance improvements. The project detail tables shall provide the related specific project information.
Quality Assurance (QA) Spreadsheet #
FOScore software has the capability to produce a Quality Assurance Spreadsheet in Excel as well as import changes made to the spreadsheet directly into the software dataset.
Quantity #
Determined by count and field estimating.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) #
Uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods.
Recommended Action Date or Time Frame #
The date by which a specific deficiency should be scheduled for correction (see Funding Needs entry for more information).
Regional Factor #
A unit cost assigned to each component, assembly and system includes cost adjustments for the specific geographical location of the building or facility, known as the Regional Factor. This metric is determined by national databases and the CannonDesign cost estimation and bid results database.
Renewal #
The regeneration of one or more of an asset’s systems or components to bring the standard back to a new or acceptable condition. This could be considered functional but is contextually dependent on the description of the renewal, as certain ‘Refresh’ tasks could be interchanged with ‘Renewal.’
Renewal and Deferred Maintenance (RDM) #
Generally communicated with inclusion concepts of related cost and timing.
Renovation #
The general description of activities intended to extend the service life of a facility or portion of a building, system, or component. Renovation may include repair, replacement, or modernization to more current requirements, standards, codes, regulations, efficiencies or other enhancements.
Replacement #
The process of removal of an existing building component, assembly, or system and the installation of a new component, assembly, or system.
Repair #
Restoring a component, assembly, or system in a facility to its original condition.
Repair Factor #
Determined by an assessor during the on-site assessment. An assigned repair factor of 100% illustrates specifying full replacement of the assessed component or system.
Risk of Failure #
The current potential of a component, assembly, or system to malfunction or cease operation as intended.
Rolling Clock #
Ten-year total Deferred Maintenance Deficiencies (DMDs) include the 5-year total DMD (cumulative values). The 10-year DMD total may be revised if 5-year needs are cured within the assessment 5-year window. As each year passes, remaining deficiencies generally have action timeframes reduced by one year, which may impact the priority. The industry-standard recommendation is to perform a reassessment in 5-years to capture new 10-year needs.
Roof Square Footage #
The total space in square feet calculated from the exterior perimeter of the roof edge.
Rubric #
A framework guiding the collection of data for scoring. The Facility Suitability Assessment rubric outlines what Measures are included under each KPI and identifies which Category they are in. A rubric also identifies the collection method and type of scoring used to collect a Measure.
Suitability Standard #
A set of approved and/or ideal requirements. In a Facility Suitability Assessment (FSA) the Standard is the foundation against which the Measure is compared to determine how the Measure is scored. Example: a Standard for the size of a room is 500 square feet. A room is measured during an FSA and is 480 square feet. By comparing the actual size of the room to the Standard the room is determined to not conform to the requirement. The room then is assigned the score outlined in the Rubric for not meeting the Standard.
System #
A group of components, assemblies and/or equipment that form an operational portion of a building or facility. An example is a mechanical system, made up of many components including diffusers, assemblies that include ductwork and dampers, and equipment including air handlers, chillers, and boilers.
System Condition Index (SCI) #
An industry-standard index that objectively measures the current condition of a building component, assembly, or service system within an asset. SCI utilizes the UniFormat® classification system, and is derived from the equation SCI = Repair or Replacement Cost ÷ Replacement Value (of component, assembly, or system).
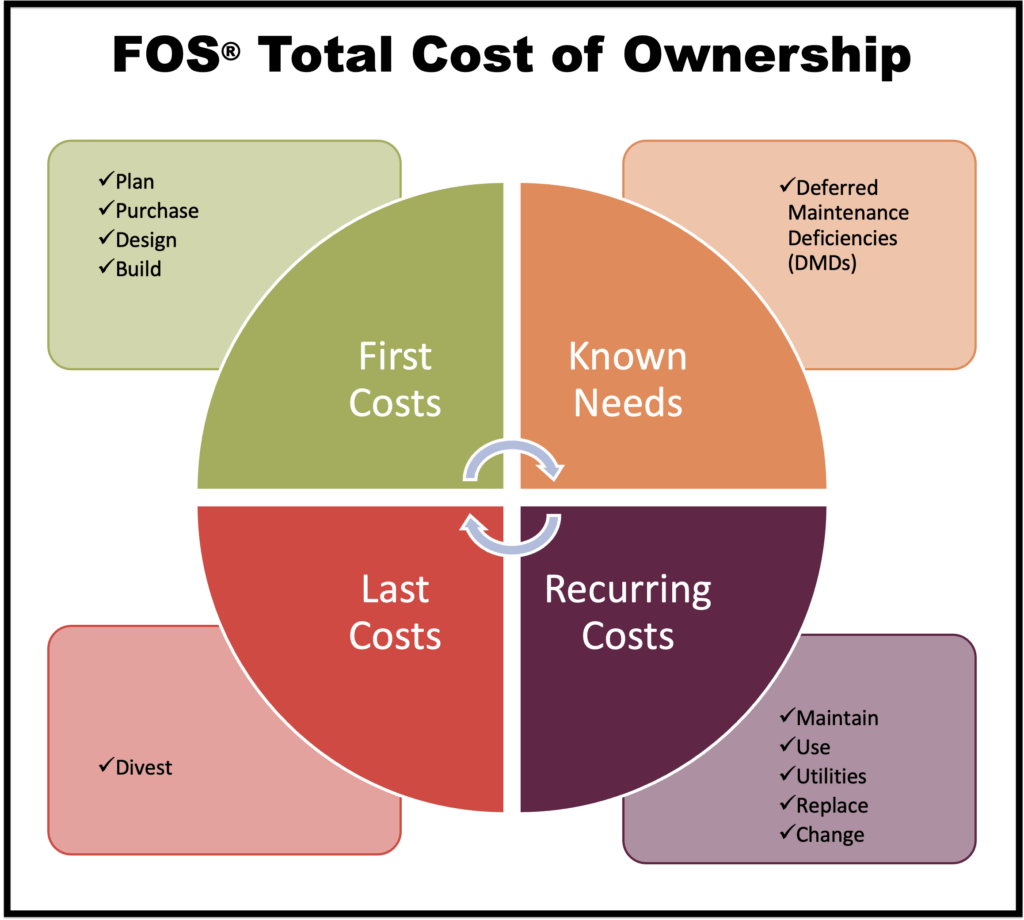
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) #
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is a business model that includes the following: The sum of all costs involved in the purchase, installation, operation, and maintenance of a given asset during its lifetime in addition to divestment costs. FOScore breaks TCO into four simplified categories–first costs, known needs, recurring costs, and last costs.
Ton #
A unit of measure used in the refrigeration and air conditioning industry to measure the rate of heat absorption. A standard ton of refrigeration is 12,000 BTU per hour. Prior to the introduction of mechanical refrigeration, cooling was accomplished by delivering ice. Installing mechanical refrigeration with a one-ton capacity replaced the daily delivery of one ton of ice.
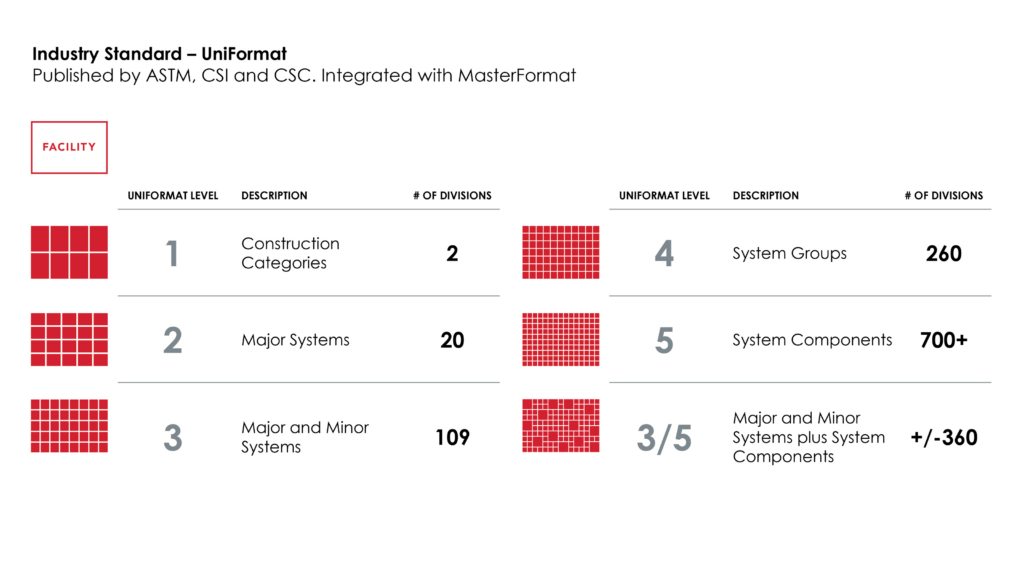
UniFormat® #
A product of the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) and Construction Specifications Canada (CSC) respectively.
Software and related assessment data shall be cataloged utilizing UniFormat® by CSI®. Assessments will be conducted utilizing industry-standard UniFormat®, as published which is integrated with MasterFormat®. The chart below illustrates five assessment levels and the related complexity of each based upon the number of divisions required to be assessed.
Unit Cost #
The price per individual component, assembly, or system in a building or facility, and measured by count (each), linear footage (LF), square footage (SF), building gross square footage (BGSF), roof square footage (RSF), stair flight (FLIGHT), stair riser (RISER), or elevator floor level (STOP).
Unit costs shall be assigned to each UniFormat® catalog deficiency item within the software platform, with an adjustment capability to suit the observed condition including difficulties of repair, adjacent work removals and replacement, confined workspace, overtime work requirements and other extraneous factors that affect the unit cost.
Useful Life or Expected Useful Life #
The period during which a building component, assembly, or system in a building or facility is expected to be useable for the purpose for which it was intended. It may not necessarily correspond to the item’s actual physical or economic life. Some building systems can continue to function well beyond their intended useful life but may be less efficient (see Beyond Useful Life entry for more information).
© Copyright 2024, FOS of CannonDesign – All Rights Reserved – Confidential and Proprietary